Choosing a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) solution isn’t just about comparing features. Security and IT leaders face complex questions: How will the PKI integrate into existing systems? Can it handle the scale and automation demands of modern infrastructure? Will it remain secure and compliant as the cryptographic landscape evolves? These aren’t abstract concerns; they directly impact operational continuity, security posture, and future scalability.
Moreover, the rise of PKI-as-a-Service (PKIaaS) introduces new possibilities and trade-offs. Should you manage PKI in-house, or is a managed, subscription-based approach more efficient? This guide dives into these pressing questions, addressing the nuances of PKI selection to help you make a decision that aligns with your organizational goals and long-term strategy.
Is Your PKI Ready? Get the Score
Quick self-assessment for CISOs/IT—see gaps and priority fixes.
What is a PKI?
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a cryptographic framework that establishes and manages digital trust within an organization. Despite PKI’s foundational importance to the cybersecurity and compliance programs of most organizations, it is often misunderstood. PKI refers to a set of technologies that use cryptographic keys and digital certificates to enable secure communications, data encryption, and authentication. At its core, PKI ensures that entities—whether people, devices, or applications—can communicate securely and verify each other’s identity.
What are the core components of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
PKI consists of several interdependent components that work together to provide security and trust:
- Certificate Authority (CA): The trusted entity that issues and manages digital certificates. The CA acts as a root of trust, verifying the identities of entities (users, devices, applications) before issuing certificates.
- Considerations: Internal vs. external CA, hierarchical vs. mesh CA architectures, certificate policies and practices.
- Digital Certificates: Electronic documents that bind a public key to an entity, serving as digital identities. Certificates enable secure communication and authentication by verifying the identity of the certificate holder.
- Types: X.509 certificates, TLS/SSL certificates, code signing certificates, S/MIME certificates.
- Key Management: Secure generation, storage, and management of cryptographic keys are crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of the PKI system.
- Key Storage: Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), key escrow, key backup and recovery.
- Key Lifecycle Management: Key generation, distribution, rotation, and revocation.
- Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM): Automating the processes of certificate discovery, issuance, renewal, and revocation is essential for operational efficiency and minimizing security risks.
- Automation: Automated enrollment, renewal, and revocation processes.
- Integration: Integration with directory services, network devices, and security tools.
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs): These are hardened, tamper-resistant hardware devices specifically designed to secure and manage cryptographic keys. HSMs provide a high level of protection against unauthorized access and compromise, making them essential for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of the PKI system.
How is PKI Different from Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM)?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there’s a crucial distinction between Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM). Think of PKI as the overarching system for establishing and managing digital trust, while CLM focuses specifically on the operational processes related to digital certificates within that system.
Here’s a breakdown:
PKI:
- Establishes the foundation of trust: PKI defines the policies, procedures, and technologies for managing digital certificates and cryptographic keys.
- Provides the infrastructure: This includes components like Certificate Authorities (CAs), Registration Authorities (RAs), and certificate repositories.
- Enables core security functions: Supports authentication, encryption, data integrity, and non-repudiation.
CLM:
- Focuses on certificate lifecycle operations: This includes certificate discovery, issuance, renewal, revocation, and monitoring.
- Automates certificate management tasks: Reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and improves efficiency.
- Enhances security and compliance: Helps prevent certificate-related outages, security breaches, and compliance violations.
Why You Need Both:
While PKI and CLM are distinct concepts, they are intertwined and complementary. In fact, CLM is actually an essential component of a comprehensive PKI solution that is aligned with best practices. PKI establishes the overall infrastructure, policies, and procedures for managing digital certificates and cryptographic keys. It defines how certificates are issued, revoked, and used within your organization.CLM provides the operational capabilities to manage certificates throughout their lifecycle. This includes discovery, issuance, renewal, revocation and monitoring of all your organization’s internal and external certificates.
When using a PKI without a CLM solution, organizations often struggle with a variety of issues. The most common issues we see from organizations with an effective CLM are a lack of visibility, highly manual processes, insufficient compliance and high costs. Think of it this way: PKI provides the foundation and framework for digital trust, while CLM provides the tools and processes to manage and maintain that trust effectively.
For a deeper dive into the fundamentals, see our full guide on what PKI is in cyber security.
Comparing Leading PKI Solutions: Venafi, Keyfactor, HID Global
The PKI market offers a number of trusted players, each tailored to specific use cases. Three of Accutive Security’s preferred partners that our clients report high satisfaction with are Venafi, Keyfactor, and HID PKI.
CyberArk Identity Security (formerly Venafi)
Focus: Machine Identity Security as part of the CyberArk identity security portfolio. Venafi specializes in securing machine identities, including those used in cloud workloads, containers, and IoT devices. In 2024, Venafi was acquired by CyberArk, a global leader in identity and access management solutions such as privileged access management. With the Venafi acquisition, CyberArk has significantly bolstered their capabilities for securing machine identities, in addition to their longstanding strength with human identity security.
- Strengths: Automated certificate discovery and management, strong integration with DevOps tools and cloud platforms, robust security features. The integration with CyberArk’s suite of IAM tools provides a significant advantage for existing CyberArk customers.
- Best for: Organizations with large-scale deployments of machines and a need for automated certificate lifecycle management across complex environments.
Keyfactor
Focus: Scalable PKI solutions, including PKI-as-a-Service (PKIaaS), to simplify infrastructure management. Keyfactor is also a major contributor to and supporter of open-source PKI, particularly through its involvement with EJBCA and the PKI Consortium.
- Strengths: Centralized certificate management, automated certificate lifecycle automation, support for hybrid and multi-cloud environments, flexible deployment options.
- Best for: Organizations seeking a comprehensive PKI solution with flexible deployment options and strong automation capabilities.
HID Global
Focus: Identity and Access Management (IAM) with a strong emphasis on PKI for secure authentication and access control.
- Strengths: Robust authentication solutions, strong focus on compliance and security, expertise in industries with strict regulatory requirements (e.g., government, healthcare, finance).
- Best for: Organizations that prioritize strong authentication and access control, need to comply with stringent regulations, and require a PKI solution that integrates seamlessly with their IAM infrastructure.
Each of these leading solutions offers robust capabilities, but choosing the right PKI requires more than just a feature comparison. You need to determine how well the solution aligns with your infrastructure, scales with your organization’s growth, integrates seamlessly into your existing systems, and supports your compliance and security objectives. The following considerations will help you evaluate these critical factors and make a confident, strategic choice.
Key Considerations for Choosing your PKI Solution
1. Considering your PKI Architecture Needs
A well-designed PKI architecture is essential for meeting your specific security and compliance needs. Consider the following components:
- Certificate Authority (CA): Will you use an internal or external CA? How many CAs do you need? What trust model will you use (hierarchical, mesh)?
- Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM): Choose a robust CLM solution to automate certificate management tasks and ensure visibility and control.
- Key Management System (KMS): Implement a secure KMS to protect your cryptographic keys.
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs): Use HSMs to provide a high level of security for your most sensitive keys.
For most organizations that lack a mature PKI, starting with a comprehensive PKI assessment is recommended.
2. Avoiding Infrastructure Incompatibility
PKI solutions must seamlessly integrate with your existing IT ecosystem, which can include a mix of legacy systems, modern cloud platforms, and specialized devices. Incompatibility can lead to deployment failures, security gaps, and operational disruptions.
Integration Challenges:
- Legacy Systems: Integrating with older systems that lack modern APIs can require custom development or middleware solutions.
- Multi-Cloud Environments: Ensuring consistent certificate management across different cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) can be complex.
- IoT Devices: Many IoT devices have unique security requirements and may use lightweight protocols that require specialized PKI configurations.
Solutions:
- API-driven integration: Prioritize PKI solutions with robust APIs for integration with IAM systems, DevOps pipelines, SIEM solutions, and other critical tools.
- Backward compatibility: Ensure the PKI solution supports legacy systems and protocols.
- Cloud-native support: Choose a solution with native support for major cloud platforms and containerization technologies.
3. Finding the Right Deployment Model
Selecting the appropriate deployment model is crucial for balancing cost, control, and scalability.
| PKI Model | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| On-Premises PKI | Maximum control, compliance with strict data residency requirements. | High upfront costs, requires significant internal expertise, potential scalability limitations. |
| Cloud-Based PKI (PKIaaS) Types: Managed PKI, Hosted PKI, Cloud-Native PKI |
Scalability, cost-effectiveness, reduced operational overhead, access to advanced features. | Potential data sovereignty concerns, vendor lock-in, reliance on provider’s security and SLAs. |
| Hybrid PKI | Combines the control of on-premises with the scalability of the cloud. | Increased complexity, requires careful planning to ensure seamless integration and synchronization between environments. |
PKIaaS simplifies deployment and management for organizations lacking in-house expertise. Providers like Venafi, Keyfactor and HID offer PKIaaS solutions with customizable policies, automated updates, and compliance-ready configurations.
4. Ensuring Scalability and Automation
As organizations adopt DevOps, IoT, and multi-cloud strategies, the number of certificates grows exponentially. The impending disruption of 90-day (and 45-day) certificate validity periods is expected to bring more than 5 times more certificate renewals for IT teams. For most organizations, manually managing 5x more renewals is not possible without incurring significant risk and resource constraints. Additionally, the need for quantum resistant algorithms is expected to have broad impacts across the entire PKI framework from CLM to HSMs. Establishing crypto agility to rapidly adopt and deploy new algorithms will be key.
What to Look For:
- Does the PKI support a wide range of cryptographic algorithms, enabling you to quickly adopt quantum resistant cryptography?
- Does it support the unique requirements for IoT and mobile device certificates, including lightweight protocols and diverse formats?
- Can it scale to support thousands of certificates for IoT, cloud services, and internal devices?
- Does the PKI support high availability and disaster recovery to maximize reliability and performance?
- What monitoring and reporting capabilities does the PKI have?
Without automation, certificate renewal delays and expired certificates can lead to outages, security vulnerabilities, and compliance violations. Scalability ensures that the PKI can support increasing workloads without compromising performance.
Venafi’s automation capabilities make it ideal for organizations managing thousands of certificates across multi-cloud environments, while PKIaaS providers streamline scalability by offloading infrastructure burdens to the vendor.
5. Staying Ahead of Compliance Requirements
Compliance is a moving target, with regulations like GDPR, FIPS 140-2, HIPAA, GLBA, and PCI DSS evolving regularly. A PKI solution that fails to adapt to new standards could leave your organization vulnerable to data breaches, fines and reputational damage. The rapid advancement of quantum computing presents major challenges for existing cryptographic algorithms underlying digital trust. Adopting crypto agility will enable your organization to quickly adopt new quantum-resistant algorithms, such as CRYSTALS-Kyber.
What to Look For:
- Pre-configured templates for compliance frameworks like GDPR or CMMC.
- Detailed audit trails that log certificate issuance, revocation, and lifecycle events.
- Reporting tools that simplify documentation for audits and regulatory submissions.
Regulatory non-compliance can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Audit readiness requires detailed logging and reporting capabilities, along with built-in compliance configurations.
PKIaaS providers are embedding compliance features directly into their platforms. By outsourcing compliance maintenance, organizations can focus on operational goals without worrying about evolving standards.
6. Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The true cost of a PKI solution goes beyond licensing fees. You must account for deployment, customization, ongoing management, and scaling costs.
What to Consider:
- What are the upfront implementation costs, including integration with existing systems?
- How many certificates does your organization use now, and what is the projected usage in the future?
- How does the solution scale cost-effectively as your certificate needs grow?
Hidden costs, such as extensive customization or high support fees, can quickly turn an affordable solution into an expensive liability. PKIaaS offers a predictable subscription model, but it can end up being more expensive than an on-premises solution in some cases.
On-premises PKIs often have higher upfront costs but lower long-term expenses for organizations with stable infrastructures. PKIaaS, on the other hand, provides predictable pricing but may introduce premium costs for advanced configurations or high-volume certificate issuance.
Build Before you Commit: Designing a PKI Proof of Concept (POC)
Don’t make a costly mistake by choosing a PKI solution that doesn’t meet your needs. A Proof of Concept (POC) allows you to test a PKI solution in a real-world environment before committing to a full-scale implementation. This helps you identify potential compatibility issues, performance bottlenecks, and missing features early on, saving you time, money, and frustration down the road.
Accutive Security Innovation Lab: Your PKI Testing Ground
The Accutive Security Innovation Lab provides a controlled environment for conducting comprehensive POCs. Our lab mirrors your infrastructure, allowing you to test multiple PKI solutions, evaluate their performance, and ensure they integrate seamlessly with your existing systems.
Benefits of Using the Accutive Security Innovation Lab
- Accelerated Evaluation: Quickly test and compare different PKI solutions in a realistic environment.
- Reduced Risk: Identify potential issues and mitigate risks before making a significant investment.
- Hands-on Experience: Gain practical experience with the solution and its features.
- Improved Decision-Making: Make informed decisions based on real-world testing and evaluation.
- Faster Deployment: Reduce implementation time by familiarizing your team with the chosen solution in advance.
What you can expect at the Accutive Security Innovation Lab
- Hosted Lab Environments: Save time and resources by using fully equipped labs, avoiding the hassle of building your own setups.
- Realistic Testing: Simulate real-world scenarios to verify tool compatibility and prevent integration issues.
- Access to Leading PKI Solutions: Leading PKI solutions from global cybersecurity leaders like Keyfactor, Venafi, Thales and HID are pre-loaded in the Innovation Lab for demos, proof of concepts and testing.
- Product Demos: Experience solutions firsthand to see how they perform, enabling confident and informed decisions.
- Training: Train your team on the selected PKI solution, significantly reducing ramp-up time and ensuring a smoother deployment.
Start building a PKI proof of concept for free!
Scaling your PKI Architecture: From Single to Multi-Tier and Zero Trust PKI
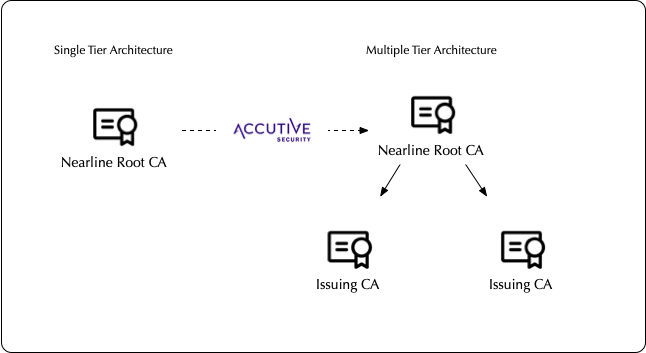
Single-Tier PKI
Traditional PKI often starts with a single-tier architecture, where a single Certificate Authority (CA) issues and manages all certificates for the organization. This approach is simple to implement but can become a bottleneck as the organization grows and the number of certificates increases.
- Limitations:
- Scalability: Limited scalability as the single CA becomes a central point of failure and performance bottleneck.
- Security: A single point of compromise can jeopardize the entire PKI system.
- Certificate Volume Concerns : Managing a large number of certificates with a single CA can be cumbersome and inefficient.
Multi-Tier PKI
To address these limitations, organizations often move to a multi-tier PKI architecture. This involves establishing a hierarchy of CAs, with a root CA at the top and subordinate CAs issuing certificates for specific departments, applications, or use cases.
- Benefits:
- Improved Scalability: Distributes the workload across multiple CAs, improving performance and resilience.
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the impact of a single CA compromise.
- Delegated Administration: Allows for decentralized certificate management, empowering different teams or departments to manage their own certificates.
- Increased Flexibility: Supports different certificate types and use cases with specialized CAs.
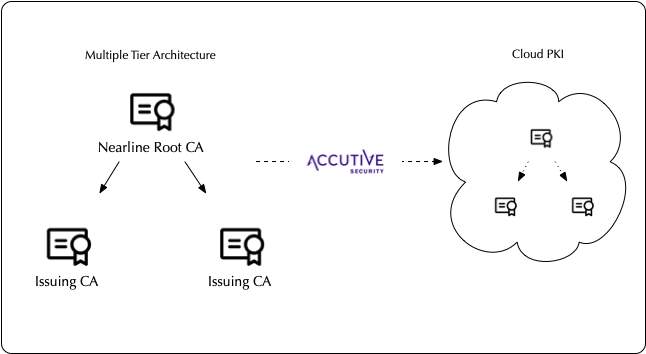
Zero Trust PKIaaS
The rise of cloud computing, remote work, and sophisticated cyber threats has driven the adoption of Zero Trust security frameworks. Zero Trust PKIaaS takes PKI to the next level by integrating it with a Zero Trust security model.
Key Principles:
- Never trust, always verify: Every user, device, and application must be authenticated and authorized before accessing resources.
- Least privilege access: Grant only the minimum necessary permissions to users and devices.
- Continuous monitoring: Continuously monitor and verify access to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
Benefits of Zero Trust PKIaaS:
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the attack surface and mitigates the risk of lateral movement in case of a breach.
- Improved Compliance: Helps meet regulatory requirements for strong authentication and access control.
- Simplified Management: Leverages the scalability and flexibility of cloud-based PKIaaS solutions.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Minimizes the need for on-premises infrastructure and dedicated PKI expertise.
Choosing a PKI Solution That Scales with Your Needs
When choosing a PKI solution, it’s essential to look beyond the basic features and consider the broader needs of your organization. Here are key takeaways to guide your decision:
- Think Long-Term: Select a solution that can adapt to your organization’s evolving needs, including future growth, new technologies, and changing security threats.
- Prioritize Scalability and Automation: Ensure the solution can handle increasing certificate volumes and automate certificate lifecycle management to minimize risks and improve efficiency.
- Embrace Cryptographic Agility: Choose a solution that supports a wide range of cryptographic algorithms and can adapt to new standards as they emerge, especially with the approaching threat of quantum computing.
- Address Compliance Requirements: Ensure the solution helps you meet relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as FIPS 140-2, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others.
- Consider Deployment Flexibility: Evaluate different deployment models (on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid) and choose the one that best aligns with your organization’s needs and risk tolerance.
- Don’t Underestimate Integration: Ensure seamless integration with your existing infrastructure, including legacy systems, cloud platforms, and security tools.
- Conduct Thorough Testing: Perform a Proof of Concept (POC) to validate the solution’s capabilities and compatibility with your environment.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a PKI solution that not only meets your current needs but also provides a solid foundation for secure and trusted digital operations in the years to come.













Comment